The Ultimate Guide to Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Optimal Health
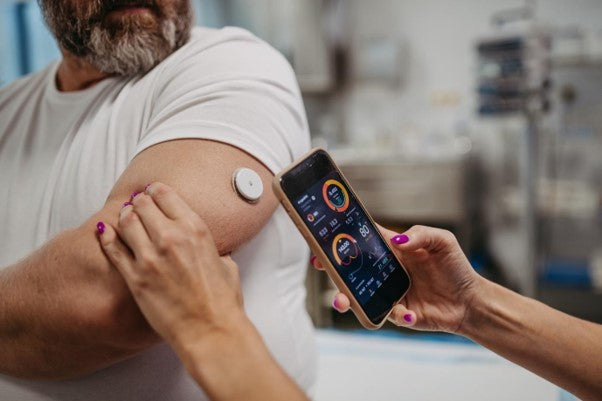
Understanding Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) symbolizes a major advancement in personal health technology. It enables raw, continuous insight into glucose levels, thus facilitating tailored health control and shedding light on our body's unique responses to various facets of lifestyle including food and exercise.
Who Can Benefit from a Continuous Glucose Monitor?
Continuous Glucose Monitoring isn't just for those with Type 1 diabetes who rely on it to balance insulin levels—a crucial part in preventing severe distortions in blood glucose levels.
CGMs can bring value to anyone, and here's why:
They serve as a personalised tool to understand how different types of food affect your blood sugar, as responses can vary on an individual basis. This personalized data drawn from CGM can help contour an appropriate diet, promoting stable blood sugar levels and potentially improving overall health.
Additionally, CGMs are instrumental in enhancing metabolic flexibility—that is, our body's ability to shift efficiently between burning glucose and fat for energy. This might assist in managing weight, fatigue, and hunger.
Most notably, these devices can offer early detection of metabolic dysfunction, often showcasing changes in glucose control years before conventional tests can identify it, providing an opportunity for preemptive measures. So, whether managing diabetes or simply improving daily health, CGMs offer valuable insights.
The Vital Role of Blood Sugar in Health
Bloodstream glucose is a reliable metric of our metabolic health. Abnormal glucose levels may lead to decreased energy, cognitive function impairment, and over time, increase risk of chronic illnesses like diabetes or heart disease[1]. CGM functions as a watchman, identifying unnoticed glucose spikes and dips suggesting a need for dietary or lifestyle modification[2].
